1 What is a Thread in Java
A thread is light weight process that can execute simultaneously. Multithreading in java allows multiple threads to run simultaneously.
- A program can be divided into two or more parts that can run concurrently and each part of such program is known as
thread . - In a simple word,
thread is a lightweight sub-process. - It is
a smallest unit of processing. - When
these thread s execute concurrentlyfor accomplishing a task is known multithreading. - In multithreading, each thread defines a separate path of execution.
- In multithreading, every thread has a priority between 1 to 10. Thread with
highest priorityget preference over lower priority thread for execution.

In a java programming, Thread is a predefined class within a java.lang package.
Operating system (OS) can contain multiple
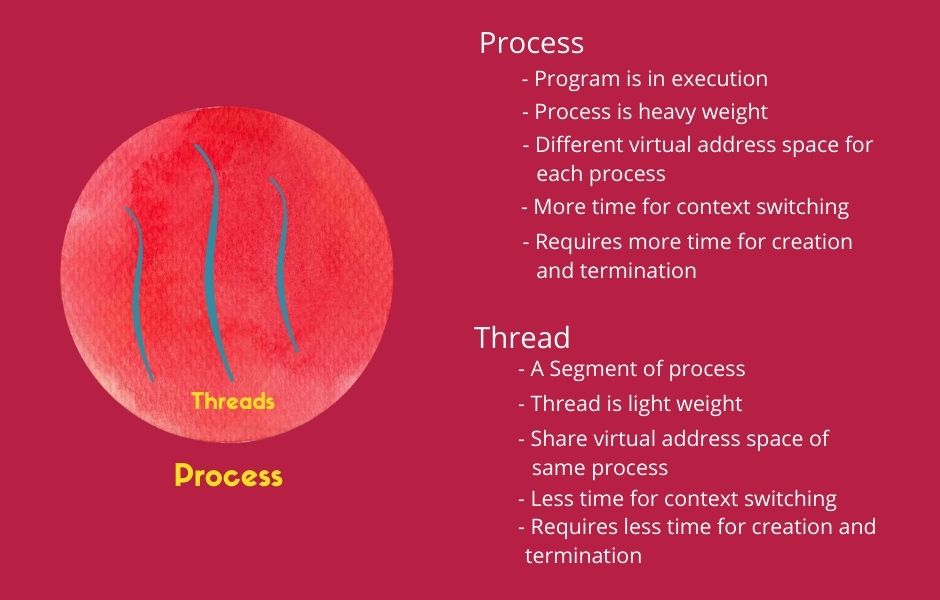
2 Difference between Process and Thread
| Process | Thread |
|---|---|
| A process has their own virtual address space. | Threads are entities within a process it uses its virtual address space of process. |
| Two processes running on the same system at the same time do not uses address space. | Two threads running within a process uses the same address space. |
| Every process has its own data segment | All threads within the process uses the same data segment of process. |
| In multiprocessing, processes use inter process communication techniques to interact with other processes. | In multithreading, threads do not uses inter process communication techniques because they not uses separate address spaces. They share the same address space therefore, they can communicate directly with other threads within process. |
| Processes have considerable overhead. | Threads have almost no overhead; |
| Process is heavy weight. | Threads are light weight process (LWP). |
| Process contains much information about system, resource. | Threads carry less state information than process |
| When we create a child process from a parent process then it requires duplication of the resources of parent process. | No duplication of resources is required when we create a child thread from main thread. |
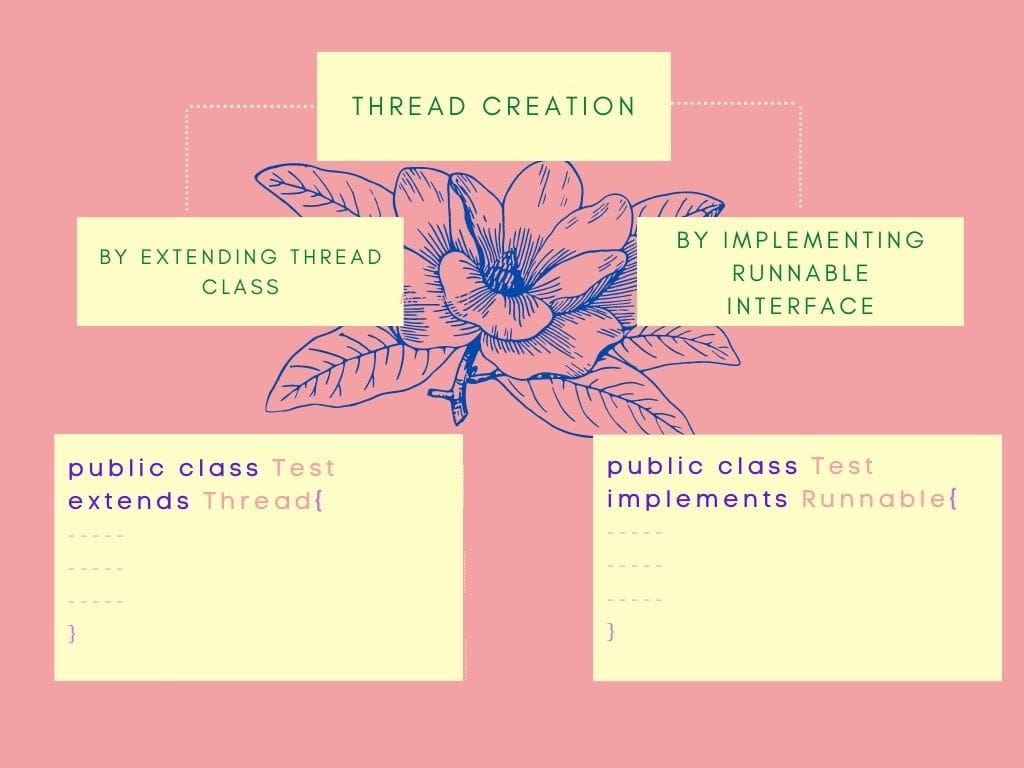
3 How to create a thread in Java
We can create a thread by two ways:
- By extending Thread
- By implementing Runnable interface
Lets see multithreading in java with example
A Creating Thread By Implementing Runnable Interface
- We can create a thread by creating a class that implements the Runnable interface.
- To implement Runnable, a class only need to implement a single method called run().
- Inside run () we will define the code that constitute the new thread.
- When a new thread creates, it do not executes until we call its start () method. When start () method executes it call to run() method.
Below is the multithreading program in java with implementing runnable interface
Example: Print hello to illustrate multithreading example in java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public class ThreadTest1 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ System.out.println("Hello from run"); } public static void main(String[] s){ ThreadTest tt=new ThreadTest(); Thread t=new Thread(tt); t.start(); } } |
Output
1 | Hello from run |
Creating more than one thread in java :- multithreading in java example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | public class ThreadTest3 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ try{ for (int i=0 ;i<10;i++){ System.out.println("Hello from run "+i); Thread.sleep(5000); } } catch(InterruptedException e){ System.out.println("InterruptedException " +e); } } public static void main(String[] s){ ThreadTest3 tt=new ThreadTest3(); Thread t=new Thread(tt); t.start(); Thread t1=new Thread(tt); t1.start(); } } |
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | Hello from run 0 Hello from run 0 Hello from run 1 Hello from run 1 Hello from run 2 Hello from run 2 Hello from run 3 Hello from run 3 Hello from run 4 Hello from run 4 Hello from run 5 Hello from run 5 Hello from run 6 Hello from run 6 Hello from run 7 Hello from run 7 Hello from run 8 Hello from run 8 Hello from run 9 Hello from run 9 |
Another Example of Thread is
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | class Demo implements Runnable { Thread t; Demo() { // creating a new, second thread t = new Thread(this, "DemoThread"); System.out.println("Child Thread= " + t); t.start(); // start a thread & call run() } public void run() { try { for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Child Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(500); // Let the thread sleep for a while. } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Child exception "); } System.out.println("exit child thread"); } } public class CreateThread { public static void main(String args[]) { new Demo(); try { for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println(" Main Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(1000); // Let the thread sleep for a while. } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main exception "); } System.out.println("exit main thread"); } } |
Result
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Child Thread= Thread[DemoThread,5,main] Child Thread: 5 Main Thread: 5 Child Thread: 4 Main Thread: 4 Child Thread: 3 Child Thread: 2 Main Thread: 3 Child Thread: 1 exit child thread Main Thread: 2 Main Thread: 1 exit main thread |
Description:
Passing “this” as
In this program, main thread
This cause the child thread terminates earlier than main thread.
B Creating Thread By extending Thread class in java
- To create a thread we will create a thread a class that extends Thread class.
- To extend Thread class, a class only needs to implement a single method called run (). This extending class must override the run() method
- Inside run () we will define the code that constitute the new thread.
- When a new thread creates, it do not executes until we call its start () method. When start () method executes it call to run() method.
Simple Thread example in java
Example: Write a thread program in java by extending thread class.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public class ThreadTest extends Thread{ public void run(){ System.out.println("Hello from run"); } public static void main(String[] s){ ThreadTest t=new ThreadTest(); t.start(); } } |
1 | Hello from run |
Multithreading in Java example programs
Example: Write a program to show multithreading in java by extending thread class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public class ThreadTest extends Thread{ public void run(){ System.out.println("Hello from run"); } public static void main(String[] s){ ThreadTest t=new ThreadTest(); t.start(); } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | Hello from run 0 Hello from run 0 Hello from run 1 Hello from run 1 Hello from run 2 Hello from run 2 Hello from run 3 Hello from run 3 Hello from run 4 Hello from run 4 Hello from run 5 Hello from run 5 Hello from run 6 Hello from run 6 Hello from run 7 Hello from run 7 Hello from run 8 Hello from run 8 Hello from run 9 Hello from run 9 |
Multithreading in java example using Thread class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | class Demo extends Thread { Demo() { super("DemoThread"); // creating a new, second thread System.out.println("Child Thread= " + this); start(); // start a thread } public void run() // entry point for new Thread { try { for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Child Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(500); // thread sleep for a while. } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Child exception "); } System.out.println("exit child thread"); } } public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { new Demo(); // call constructor try { for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println(" Main Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(1000); // thread sleep for a while. } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("main exception "); } System.out.println("exit main thread"); } } |
Result
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Child Thread= Thread[DemoThread,5,main] Main Thread: 5 Child Thread: 5 Child Thread: 4 Main Thread: 4 Child Thread: 3 Child Thread: 2 Main Thread: 3 Child Thread: 1 exit child thread Main Thread: 2 Main Thread: 1 exit main thread |
4 Thread Methods in Java
Commonly used methods of Thread class are as follows
| Sr No | Method and Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | void run() Work execute as a thread is defined in this method . |
| 2 | void start() Used to start a thred which Calls the run() method of the thread or child class. |
| 3 | static void sleep(long miliseconds) Suspend the thread for specified amount of time. |
| 4 | static void sleep(long miliseconds,int nanos) Suspend the thread for specified amount of time. |
| 5 | void join() This method is used to pause the ececution of current thread until it die. void join(). |
| 6 | void join(long miliseconds) Pause the execution of current thread for the pecified miliseconds. |
| 7 | void join(long miliseconds,int nanos) Pause the execution of current thread for the pecified miliseconds and nano seconds. |
| 8 | boolean isAlive() To checks a thread is alive or not. |
| 9 | String getName() Returns the name of the thread. |
| 10 | setName(String name) Used to set the name of thread. |
| 11 | int getPriority() Get the priority of the thread. |
| 12 | void setPriority(int priority) Set the priority of thread. |
| 13 | static Thread currentThread() Returns the reference of currently executing thread |
| 14 | long getId() Returns the id of the thread. |
| 15 | static void yield() Temporarily pause the currently executing thread and allow other threads to execute. |
| 16 | void suspend() Used to suspend the thread. |
| 17 | void resume() Used to resume the suspended thread. |
| 18 | void stop() Used to stop the thread. |
| 19 | void interrupt() Interrupts the thread. |
| 20 | boolead isInterrupted() Check whether the thead is interrupted or not |
Use of thread in java
- To Reduce the time of execution of a program
- To achieve parallel execution
Read More
How many ways to create thread in java
There are two ways to create thread in java
- By Extending Thread class
- By Implementing runnable Interface.
Types of thread in java
- Daemon thread provide services to other threads
- User defined threads Created by User
How to perform two tasks by two threads ?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | class Thread1 extends Thread { public void run() { System.out.println("Hello Friends"); } } class Thread2 extends Thread { public void run() { System.out.println("Bye Friends"); } } public class TreadExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread1 t = new Thread1(); t.start(); Thread2 t2 = new Thread2(); t2.start(); } } |
1 2 | Hello Friends Bye Friends |
Real time example of multithreading in java
- When two or more I/O operations are not dependent of each other then we can perform them by different threads.
- When tow or more Database read/write operations are not dependent then we can perform using multithreads.
- Sending OTP on mobile and email id at same time.
- Adding post on social media (fb, twitter, pintrest etc) on one click using publisher software.
- Servers are multithreaded they create separate thread to handle each request.
Java multithreading programming exercises
- Create Two threads using Thread class.
- Create Two threads using runnable Interface.
- Implement Produces consumer problem in Java.

