JSON stand for Java Script Object Notation (JSON).
JSON is not a Programming Language. JSON is a data interchange format.
Using JSON we can transfer data between client and server and server to server.
JSON is defined in RFC4627 written in 2006. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) published JSON RFC7159 in March 2014.
Later on standard updated on RFC8259 and EMCA 404
JSON media type(MIME type) is application/json
JSON file extension is <code>.json</code>
In JSON data can be in following structure
- A collection of name/value pair
- An ordered list of value
These two are the universal data structure supported by approx all programming languages. So data exchange between one language to another is easy by JSON.
JSON string example is as below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | { "squadName": "Super hero squad", "homeTown": "Metro City", "formed": 2016, "secretBase": "Super tower", "active": true, "members": [ { "name": "Molecule Man", "age": 29, "secretIdentity": "Dan Jukes", "powers": [ "Radiation resistance", "Turning tiny", "Radiation blast" ] }, { "name": "Madame Uppercut", "age": 39, "secretIdentity": "Jane Wilson", "powers": [ "Million tonne punch", "Damage resistance", "Superhuman reflexes" ] }, { "name": "Eternal Flame", "age": 1000000, "secretIdentity": "Unknown", "powers": [ "Immortality", "Heat Immunity", "Inferno", "Teleportation", "Interdimensional travel" ] } ] } |
Why use JSON?
As JSON format is text only, it can be sent to server and also can received from a server, and also can be used as a data format by any programming language.
If you receive data from a server, in JSON format, you can use it like any other JS object.
JSON Syntax
JSON syntax is derived from JS object notation syntax.
• Data is in name/value pairs
• Curly braces hold objects
• Data is separated by commas
• Square brackets hold arrays
JSON Data
JSON data is written as name or value pairs.
A name or value pair consists of a field name like this “”, and it will follow by a colon, and also followed by a value:
Example
{“name”:”Ayan” }
JSON – Evaluates to JS Objects
The JSON format is a also JavaScript objects.
In JSON, keys must be strings, written with double quotes:
JSON
{ “name”:”Ayan” }
In JSON, keys can be strings, numbers, or identifier names,
{ name:”Ayan” }
JSON with JavaScript Syntax
JSON syntax is derived from JavaScript object notation, very little extra software is needed to work with JSON within JS.
With JS you can create an object and assign data to it.
Example
Access a JavaScript object
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var myObj, x; myObj = { name: "Ayan", age: 25, city: "Mumbai" }; x = myObj.name; document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html> |
Result
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var myObj, x; myObj = { name: "Ayan", age: 25, city: "Mumbai" }; x = myObj["name"]; document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html> |
JSON Values
In JSON, values must be one of the following data types:
- a string
- a number
- an object
- an array
or one of the following literal names
- false
- true
- null

JSON String Value
String value is represented in quotation any unicode character is used to create string.
like
” ” //empty string
“Ram” //string value
“\”” // use of escape character
“\uXXXX” // unicode value
JSON Numbers
JSON allows numbers as an integer or a floating point numbers.
Example
25
24.25
3.55
3.1e3
JSON Objects
Values in JSON can be objects. It contains zero or more name value pairs in curly braces seperated by comma
Example
{
“employee”:{ “name”:”Ayan”, “age”:25, “city”:”Mumbai” }
}
JSON Array
JSON Array are surrounded by [ (squrae bracket) and zero or more values or elements are seperated by comma.
The values in array may be of different types.
Example
A composite JSON structure is also possible
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [ { "name":"Ayan Das", "age":25, "knowledge":["typing","SEO"] }, { "name":"RamBag", "age":39, "knowledge":["Coding","Web designing"] } ] |
Here a JSON array contains two objects and each object contains string, number and array values
JSON is purely a data format — it contains only properties, no methods.
- JSON need a double quotes to be used around strings and property names. Single quotes are not valid in a JSON.
- A single misplaced colon or comma can cause a JSON file to go wrong, and not working that JSON file. Always be careful to validate any data in JSON. A validate JSON using an application like JSONLint.
- JSON can be taken the form of any data type that is valid for inside JSON, not just arrays or objects. So, a single string or a number can be a valid JSON object.
- Unlike in JavaScript code in which object properties may be unquoted, in JSON, only quoted strings may be used as properties.
Converting between objects and textSection
In JSON can be set the XHR request to convert the JSON response directly into a JS object using:
request.responseType = ‘json’;
But sometimes can be receive a raw JSON string, and need to convert it to an object.
when try to send a JavaScript object across the network, then need to convert it to JSON (a string) before sending.
These two problems are so common that a built-in JSON object is available, which contains the following two methods:
- parse(): Accepts a JSON string as a parameter, and returns the corresponding JavaScript object.
- stringify(): Accepts an object as a parameter, and returns the equivalent JSON string form.
See one example of stringify()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | request.open('GET', requestURL); <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <body> <script> var person = new Object(); person.name = "Ram"; person.age = 24; person.mailIds = [ var JSONtext = JSON.stringify(person); document.write(JSONtext); </script> </body> </html> |
console.table(obj); prints array in tabular format
console.log(obj[0].name); print first objects name
for (var row in obj) will iterate each object and access its properties in name value pair
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var text = '{"employees":[' + '{"firstName":"Ram","lastName":"Das" },' + '{"firstName":"Sam","lastName":"Ghosh" },' + '{"firstName":"Ayan","lastName":"Bag" }]}'; obj = JSON.parse(text); document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = obj.employees[1].firstName + " " + obj.employees[1].lastName; </script> </body> </html> |
Sam Ghosh
JSON.parse()
A common use of JSON is to exchange data to/from a web server.
parse() is used to convert JSON data to JavaScript values
Server send data as a string. To convert this string to JavaScript object JSON.parse() method is used
Example – Parsing JSON
This text received from a web server:
‘{ “name”:”Ayan”, “age”:25, “city”:”Mumbai”}’
Use the JavaScript function JSON.parse() to convert text into a JavaScript object:
varobj = JSON.parse(‘{ “name”:”Ayan”, “age”:25, “city”:”Mumbai”}’);
Use the JavaScript function JSON.parse() to convert text into a JavaScript object:
Example
Create Object from JSON String
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var txt = '{"name":"Ayan", "age":25, "city":"Mumbai"}' var obj = JSON.parse(txt); document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = obj.name + ", " + obj.age; </script> </body> </html> |
Ayan, 25
How to access nested JSON objects
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var myObj = { "name":"Ayan", "age":25, "bikes": { "bike1":"Honda", "bike2":"Bajaj", "bike3":"Hero" } } document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML += myObj.bikes.bike2 + "<br>"; //or: document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML += myObj.bikes["bike2"]; </script> </body> </html> |
Bajaj Bajaj
JSON Arrays
EXAMPLE
Access an array value of a JSON object
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var myObj, x; myObj = { "name":"Ayan", "age":25, "bikes":[ "Honda", "Bajaj", "Hero" ] }; x = myObj.bikes[0]; document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html> |
Honda
EXAMPLE
Looping through an array using a for in loop
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var myObj, i, x = ""; myObj = { "name":"Ayan", "age":25, "cars":[ "Honda", "Bajaj", "Hero" ] }; for (i in myObj.cars) { x += myObj.cars[i] + "<br>"; } document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html> |
Honda Bajaj Hero
EXAMPLE
Looping through arrays inside arrays
Nested JSON Objects
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p id="mydemo"></p> <script> var myObj, i, j, x = ""; myObj = { "name":"Ayan", "age":25, "bikes": [ {"name":"Honda", "models":["Hornet", "xblade", "livo"]}, {"name":"Bajaj", "models":["pulsar", "neon", "X5"]}, {"name":"Hero", "models":["500", "Panda"] } ] } for (i in myObj.bikes) { x += "<h1>" + myObj.bikes[i].name + "</h1>"; for (j in myObj.bikes[i].models) { x += myObj.bikes[i].models[j] + "<br>"; } } document.getElementById("mydemo").innerHTML = x; </script> </body> </html> |
Honda Hornet xblade livo Bajaj pulsar neon X5 Hero 500 Panda
See one Example to read JSON data and show in console
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> var json = `[{ "rollno": 12, "name": "Ram", "section": "A", "branch": "CSE" }, { "rollno": 14, "name": "Mohan", "section": "A", "branch": "CSE" }, { "rollno": 15, "name": "Sohan", "section": "B", "branch": "CSE" }, { "rollno": 16, "name": "Ramesh", "section": "A", "branch": "Mech" }, { "rollno": 17, "name": "Suresh", "section": "A", "branch": "Mech" }, { "rollno": 18, "name": "Mahesh", "section": "B", "branch": "Mech" }, { "rollno": 19, "name": "Naresh", "section": "A", "branch": "ET&T" } ]`; var obj = JSON.parse(json); console.table(obj); console.log(obj[0].name); for (var row in obj) { console.log(" RollNo "+obj[row].rollno +" Name "+obj[row].name +" Section "+obj[row].section +" Branch "+obj[row].branch); } </script> </body> </html> |
Result
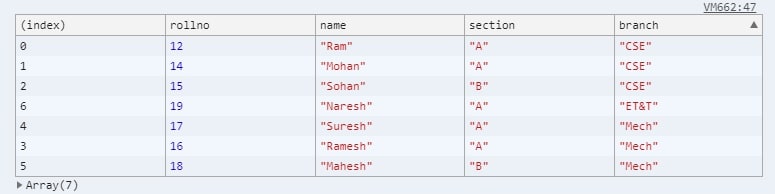
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | Ram RollNo 12 Name Ram Section A Branch CSE RollNo 14 Name Mohan Section A Branch CSE RollNo 15 Name Sohan Section B Branch CSE RollNo 16 Name Ramesh Section A Branch Mech RollNo 17 Name Suresh Section A Branch Mech RollNo 18 Name Mahesh Section B Branch Mech RollNo 19 Name Naresh Section A Branch ET&T |
JSON Vs XML
Extensible Markup Language(XML) is a Markup Language.
XML is used to access and transfer the data same like JSON.
XML uses tag to wrap content.
General structure of XML to send send data is as below
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <students> <student> <rollno>12</rollno> <name>Ram</name> <section>CSE</section> <branch>A</branch> </student> <student> <rollno>14</rollno> <name>Mohan</name> <section>CSE</section> <branch>A</branch> </student> </students> |
For above data JSON is
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [{ "rollno": 12, "name": "Ram", "section": "A", "branch": "CSE" }, { "rollno": 14, "name": "Mohan", "section": "A", "branch": "CSE" }] |
XML and JSON both are data interchange format.
In XML we have to add additional tags to carry data that is not is JSON no overhead required to carry data in JSON
JSON is based on JavaScript. XML is derived from SGML.
JSON can use Array and objects to represent and carry data. XML uses markup structure to carry data
JSON uses key value pair and array object that allows direct mapping of data structure of appropriate language.
XML allows namespace to avoid name conflicts this is not available in JSON.
JSON Formatter and Validator
JSON Formatter are used to provide structure way to JSON data.
JSON validators are tool that are used to validate JSON data.
Why JSON formatter and validator required.
If you get data from server it is in unformatted way
Like I get JSON data from url
api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=London
This will provide me weather information of London
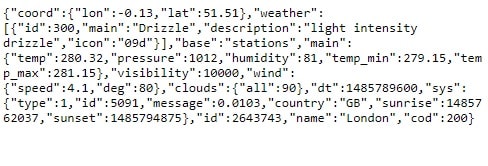
Above JSON data is difficult to read we have to format above data to make it readable.
Few online tools that can be used are
and many more
put code received from URL to any one validator that validate and structure the data so that it can be readable

