One of the important topic Exception handling in java
Here we will discuss basics of exceptions, Why Exception handling and its types.
What is Exception in Java
A unwanted event that disrupts the program execution.
In Java all Exceptions are class.
Why Exception Occurs
- Due to wrong user input
- Incorrect programming logic
Example of Exceptions
- Dividing a number by zero
5/0. It will throw ArithmeticException - Converting a String to number
Integer.parseInt("123s"). Exception It will throw NumberFormatException - Accessing beyond index in Array
a[100]when only 5 elements are in array. Throw ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
ArithmeticException on Java Program
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { int d = 0; int a = 42 / d; //Error, Arithmetic Error } } |
1 2 | Output: java.lang.ArithmeticException:/by zero at Test.main(Test.java:4) |
What is Exception Handling in Java
Exception can terminate the program execution.
To handle unwanted event and to execute rest of the program exception handling is required
On exception Java shows programmer friendly message. To show end used we need to provide custom message
How to Handle Exception in Java
Java provides keywords to handle the exception
Java exception can be handle by 5 keyword try, catch, throw, throws and finally.
- try : Any Program statement that we want to check for exception must be placed within a try block.
- catch : If the exception occurs within try block it is thrown. Your code can catch this exception (using catch) and handle it.
- throw : if an exception arises then this system-generated exception is automatically thrown by Java run time system. To manually throw an exception, throw keyword used.
- throws : A throws clause lists the type of exception that a method might throw.
- finally : In programming, we want any code must be executed after the try block completes is placed within a finally block.
Syntax:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | try{ // block of code to monitor for error } catch(Exception Type1 exob) { //Handle Type1 Exception here } catch(Exception Type2 exob) { //Handle Type2 Exception here } finally{ //block of code always execute if ther is error or not. } |
try block can be used either with a
A try can have multiple catch block.
When there is an exception in the try block an appropriate catch block is executed based on the exception.
Exception Hierarchy in java
In java programming, Exception class is a subclass of class Throwable.
Apart from the
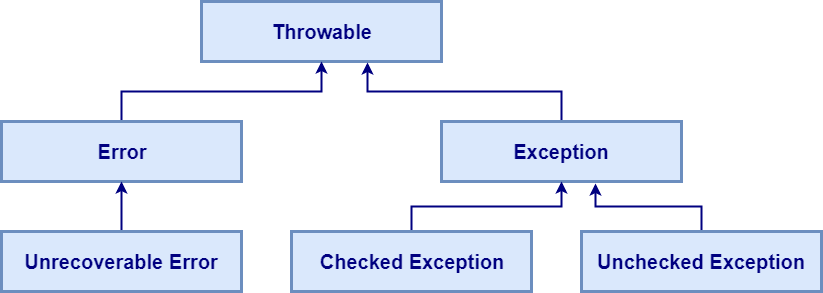
Error: In java programming, error is Unrecoverable. It occurs during compile time.
For example, if we write wrong syntax then error will generate during compile time.
Root class of exception in java
Throwable is the root class of exception in Java
Types of Exception in Java
- Checked Exception
- Unchecked Exception
Checked Exception in java
Exceptions that are checked by compiler is called checked exceptions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | import java.io.File; import java.util.Scanner; public class UserInput { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("d://test.txt"); Scanner sc=null; sc = new Scanner(f); while (sc.hasNextLine()) { System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); } } } |
On compiling above program.
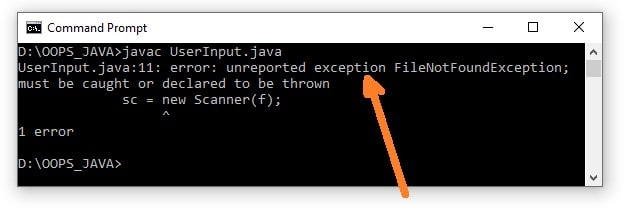
To make code executable we must surround Scanner with try and catch the FileNotFoundException.
Here is the list of some checked exception
- IllegalAccessException: in java programming, this exception occurs when access to a class is denied.
- ClassNotFoundException: this exception occurs when class not found.
NoSuchMethodException : when a requested methoddose not exist this exception occurs.- CloneNotSupportedException: in java programming
,If you are trying to use the clone method in aclasswhere Cloneable interface is not implemented, it throwsCloneNotSupportedException. Clone() method is used to createexactcopy ofa object InterruptedException : injava , when we work with multiple threads then onethread interrupts another thread.
Unchecked Exception in Java
Exception condition is not checked by compiler.
Runtime class and its sub classes are known as unchecked exception.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public class Exec1{ public static void main(String[] s){ int a=5,b=0; float c=0; c=a/b; System.out.println("Division is "+c); } } |
The compiler does not flag any error if there is an unchecked exception.
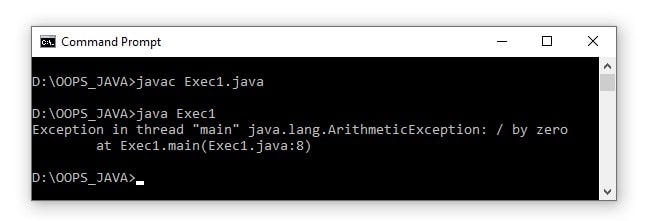
- ArithmeticException : in java programming, this exception, represent the arithmetic error, such as divided-by-zero.
- IndexOutOfBoundsException: when some type of index is out of bounds this exception occurs.
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: in java programming, this exception represents the Array index is out of bound. This condition arises when we try to access the illegal array index.
- StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: in java programming, when we access the index outside the bounds of string then this exception occurs.
- NegativeArraySizeException: when an array is created with a negative size then this exception arises.
- NullPointerException: in java programming, this exception occurs when invalid use of a null reference.
- IllegalThreadStateException: this exception occurs when the required operation is not compatible with the current thread state.
Create your own Exception: User-Defined Exception in Java
What is difference between checked and unchecked exception in java
Checked Exceptions are checked by compile at compile time.
Unchecked Exceptions are not checked by the compiler.
Advantages of Exception Handling in Java
- Error handling is separate from Regular code
- Propagating Errors Up the Call Stack
- Grouping and Differentiating Error Types
Array index out of bound exception is checked or unchecked
array index out of bound exception is unchecked Exce
Read More
- Exception Handling in Java with Examples
- Exception Handling try catch finally blocks in Java
- Throw and Throws Keywords in Java
Reference
